最新资讯
前 言
这篇文章对北斗卫星的概况做了简单总结,尤其是各个卫星的物理参数和坐标系转换。更为详细的信息可以参考中国卫星导航系统管理办公室测试评估研究中心的官网http://www.csno-tarc.cn/index/index&ce=china
This page provides an overview of the Satellites in the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS). Technical parameters of the indivdual satellites and related conventions applied within the MGEX project are summarized in the Spacecraft Characteristics section. Information about the operational status of BeiDou can be found on the website of the Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office(http://www.csno-tarc.cn/index/index&ce=china)
Satellites
The regional BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-2, earlier referred to as COMPASS) originally comprised a total of 15 launched satellites out of which 13 were fully operational in 2015. BDS-2 replacement satellites have been launched in 2016 and 2018. In mid 2015, China started the build-up of the 3rd generation BeiDou system (BDS-3) which will shall offer a fully global navigation service by 2020. In 2015/2016, five BDS-3S in-orbit validation satellites have been launched. Build-up of the operational BeiDou-3 constellation was delayed by launcher issues and finally started in November 2017.
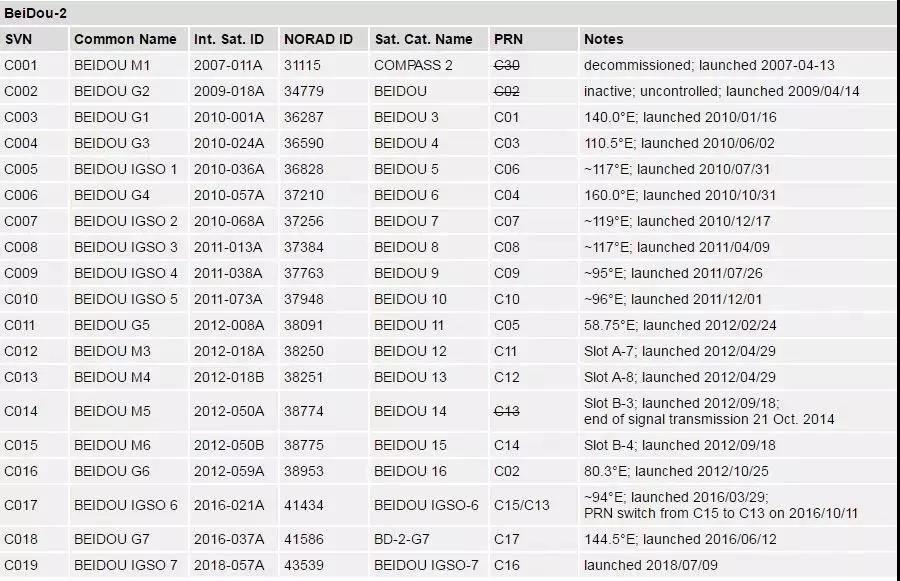
Notes:
In the absence of official space vehicle numbers (SVNs), preliminary numbers for the BDS-2 satellites have been assigend for use within the MGEX project based on the launch sequence of the respective spacecraft.
C004 was moved from 84.0° E to new position between Nov 7 and 22, 2012.
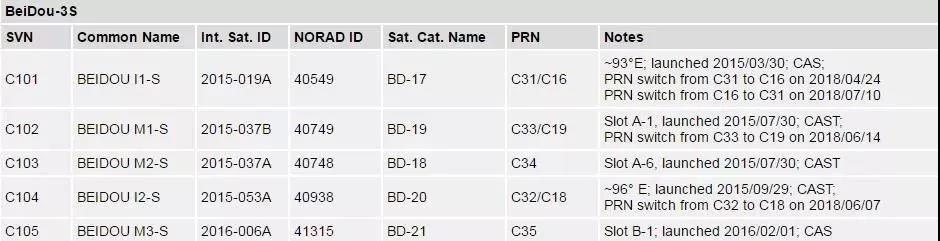
Notes:
The five BEIDOU ??-S satellites are experimental satellites of the BeiDou-3 constellation manufactured by China Academy of Science (CAS) and China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), see [5].
The association of PRN/SVN and NORAD/Int.Sat.ID numbers for BEIDOU M1-S and M2-S in the above table has been corrected on 02-Nov-2017 based on information from ILRS/SHAO.
No tracking of C35 so far
No tracking of C34 since 11 June 2018
Only B1 single-frequency tracking of C101/C16 and C104/C18 after PRN switches in April/June 2018
B1/B3 dual-frequency tracking of C101/C31 after PRN switch in July 2018
High-gain antenna measurements on 27/28 July 2018:
C101: B1/B2/B3 signal transmission
C104: B1/B3 signal transmission
C103: B1/B2/B3 signal transmission
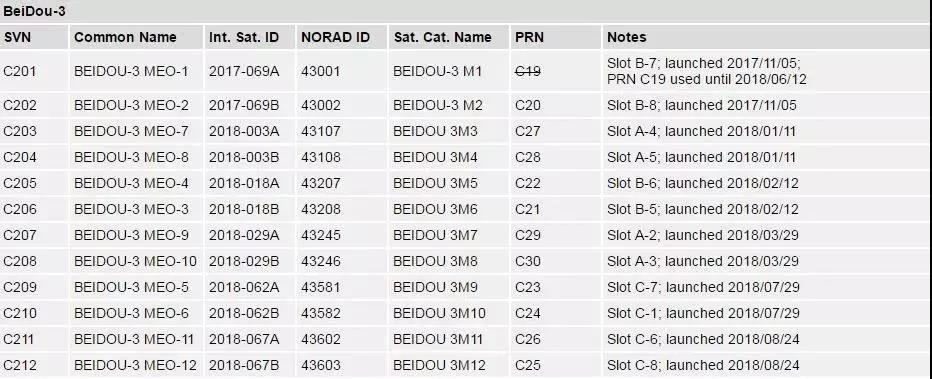
Notes:
The numbering of the spacecraft in the satellite catalog differs from the common names.
The space vehicle number (SVN) used here follows the satellite catalog number (NORAD ID).
Information on BDS-3 is preliminary and might be subject to change.
Spacecraft Characteristics
BeiDou-2
A comprehensive collection of technical information with associated references for the BeiDou-2 satellites can be obtained at the CNSS page of ESA's eoPortal .
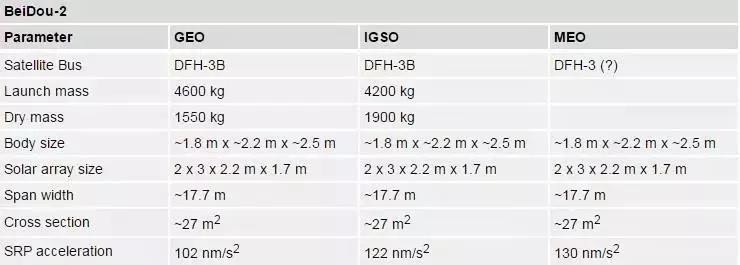
The BeiDou-2 spacecraft are equipped with broadband GNSS antennas for the B1, B2, and B3 frequency bands as well as a laser retroreflector array (LRA) for satellite laser ranging.
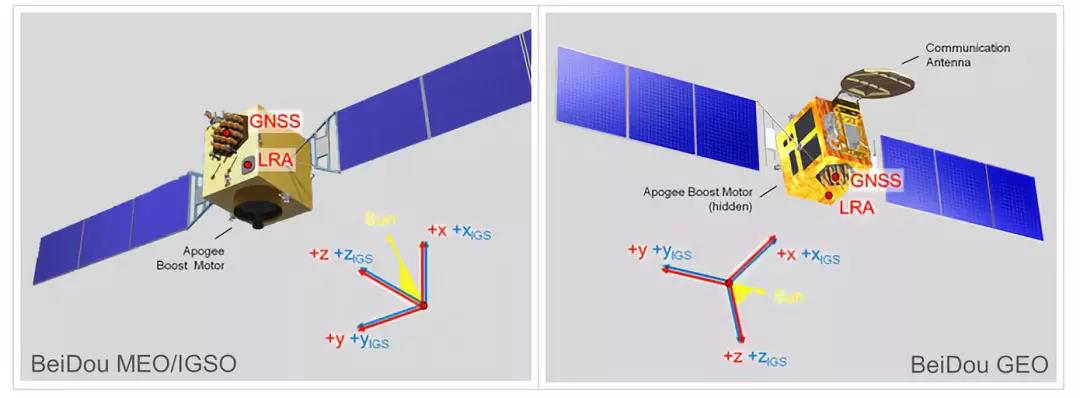
Fig. 1 Spacecraft reference system and sensor location for the IGSO/MEO (left) and GEO satellites (right) of the BeiDou-2 regional navigation system. Reproduced from DOI 10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.019 with permission of Elsevier; satellite images courtesy CSNO.
Phase center coordinates of the BeiDou-2 GNSS antenna and the LRA as recommended for use within the MGEX project are provided in the following table. A machine-readable version of the phase center offset information for each satellite is provided as part of the IGS14 ANTEX product.
All values refer to the IGS-specific spacecraft coordinate system illustrated in Fig. 1. This system is aligned with the main body axes and originates in the plane opposite to the antenna. For all three spacecraft types
the +zIGS-axis is oriented along the boresight direction of the antenna,
the +yIGS-axis is parallel to the rotation axis of the solar panels, and
the +xIGS-axis completes a right handed system.
The detailed orientation of the +xIGS and +yIGS-axes for the BeiDOu-2 satellites is defined as shown in the drawings. The GNSS antenna is shifted in +xIGS-direction relative to the center of the front panel, while the LRA is located in the -xIGS/-yIGS-corner. On GEO satellites, the +xIGS-panel holds the C-band telecommunication antenna.
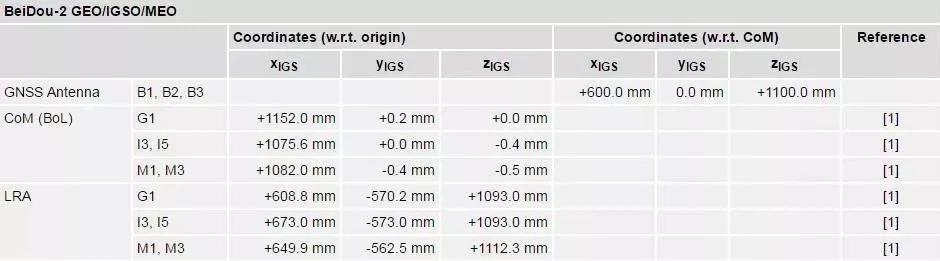
For the modelling of satellite laser ranging measurements nominal coordinates of the effective LRA reflection point have been specified by the China Satellite Navigation Engineering Center as part of the ILRS mission support request.
Due to a lack of publicly available antenna phase center offsets for the BeiDou-2 satellites, conventional values of (+0.6 m, 0.0 m, +1.1 m) are recommended for orbit and clock determination of the BeiDou-2 GEO/IGSO/MEO satellites until further notice. The values provide a first estimate of the actual phase center relative to the center of mass based on the images and models.
Based on actual BeiDou-2 GNSS observations, refined x-offsets of about +0.55 m values and z-offsets of 3-4 m and 2.0-2.5 m have been determined in [2] for the BeiDou-2 IGSO and MEO satellites, respectively, using a ionosphere-free B1/B2 combination. Even larger z-offsets were obtained for the ionosphere-free B1/B3 combination.
The attitude of the BeiDou-2 satellites is actively controlled to orient the +zIGS axis towards the Earth. For the MEO and IGSO satellites a yaw steering attitude is employed, in which the satellite is continuously rotated about the +zIGS axis to maintain the yIGS-axis perpendicular to the plane made up by the Sun, Earth, and satellite. Similar to the IGS satellites, the +xIGS-axis is pointed towards the sun-lit hemisphere. For the GEO satellites an orbit normal mode is adopted, in which the +yIGS is oriented perpendicular to the orbital plan. The orbit normal mode is also employed by the MEO/IGSO satellite when the Sun elevation above the orbital plane is less than about 4°. An overview of BeiDou-2 attitude modes and related mathematical formulations are provided in [3]. Mode transitions at low β-angles are further discussed in [4].
The latest BDS-2 IGSO satellite C017 does not enter orbit normal mode. F. Dilssner (ESOC) developed an attitude model for this satellite [6] and reports that the MEO satellite C015 and the IGSO satellite C005 follow also this attitude law since October 2016 and March 2017, respectively.
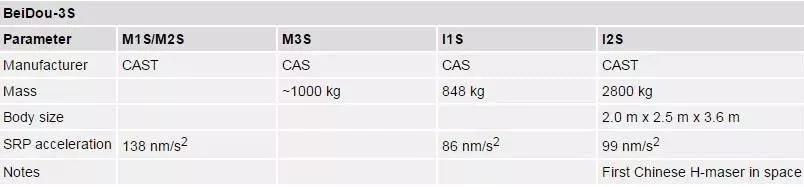
BeiDou-3S
BeiDou-3S stands for five BeiDou-3 test satellites launched in 2015/2016. They transmit legacy B1 signals similar to the BeiDou-2 satellites as well as modernized signals in the L1, E5, and B3 band.
Manufacturer satellite antenna phase center offsets as well as SLR retroreflector offsets for C101 - C104 are published in [5]. The M1S/M2S satellites are equipped with an additional fold-out phased array antenna. However, it is unknown which navigation signals are transmitted by this antenna.
BeiDou-3
[1] ILRS BeiDou (COMPASS) Center of Mass Information References
[2] Dilssner F., Springer T., Schönemann E., Enderle W.; Estimation of satellite antenna phase center corrections for BeiDou. IGS Workshop, Pasadena, California, USA (2014).
[3] Montenbruck O., Schmid R., Mercier F., Steigenberger P., Noll C., Fatkulin R., Kogure S., Ganeshan A.S. (2015) GNSS satellite geometry and attitude models. Advances in Space Research 56(6):1015-1029. DOI 10.1016/j.asr.2015.06.019
[4] Dai X., Ge M., Lou Y., Shi C., Wickert J., Schuh H. (2015) Estimating the yaw-attitude of BDS IGSO and MEO satellites. Journal of Geodesy 89(10):1005-1018. DOI 10.1007/s00190-015-0829-x
[5] Zhao Q., Wang C., Guo J., Wang B., Liu J. (2018) Precise orbit and clock determination for BeiDou-3 experimental satellites with yaw attitude analysis. GPS Solutions 22:4.DOI 10.1007/s10291-017-0673-y
[6] Dilssner F. (2017) A note on the yaw attitude modeling of BeiDou IGSO-6
_____________________________
本文转自 测绘学报
如需转载,请注明出处!
联系方式:0731-89928802(夏老师)| 技术咨询:0731-89928801转8055(张老师)| 传真:0731-89928802
邮 箱:office@gnssopenlab.org | 地 址:湖南省长沙市高新区尖山路39号中电软件园16栋 湘ICP备11010394号-3
